If you feel like you don’t have enough time to exercise, maybe it’s time to try high-intensity interval training (HIIT). HIIT is a broad term for workouts that involve short bursts of intense exercise alternated with low intensity recovery periods. One of the biggest advantages of HIIT is that you can get maximal health benefits in minimal time, making it a very time-efficient way to exercise. HIIT training workouts provide fitness benefits just as traditional exercise bouts, but tend to burn more calories, especially for hours after the workout.
HIIT training can be modified for people of all fitness levels and special conditions including overweight and diabetes. The workouts can be performed with all exercise modes including cycling, walking, swimming, body weight training and more. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends performing HIIT workouts with a specific ratio of exercise to recovery. For example, a 1:1 ratio of the exercise to recovery might be 3 minutes of hard work followed by a 3 minute recovery. Because of the intensity of the workout, only 1-2 sessions a week are recommended, with several days rest in between.
A personal trainer can help you determine the best protocol and ratio of work to rest for incorporating HIIT training into your individual workout routine. Persons with certain health conditions (Hashimotos, Hypothyroidism, high blood pressure, particular heart conditions) should not engage in HIIT training . Taking into consideration your medical history, exercise history and personal preferences, our qualified trainers can help you get results.
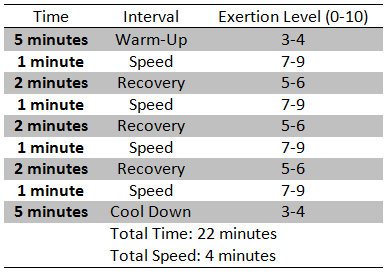
A sample program with one minute work and 2 minutes recovery is below. Using a Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) of 0-10 with 0 being no exertion and 10 being the highest, walk or jog/run on the treadmill or outdoors to give it a try.